Service References or WCF comes from VS 2008 and above with an extension as .svc and Web References are their from the beginning as .asmx.
The main difference between WCF service and Webservice while consuming, we need to add them in solution as reference to access them.
Add Web Reference is a wrapper over wsdl.exe and can be used to create proxies for .NET 1.1 or 2.0 clients. This means we are pointing to a WCF service you have to be pointing to an endpoint that uses basicHttpBinding.
Add Service Reference is a wrapper over svcutil.exe and also creates clients proxies (and additionally web.config entries). These proxies, however, can only be consumed by .NET 3.0+ clients.
Below image will show you how to add web reference from Service Reference. Right click theService References from solution explorer, then select advance button on Add Services windowyou will get to the form as in below image and then will be able to add Web Reference via Addweb Reference window..
But there is some things which changed in VS2010 about adding web references to a class library. So in VS 2010 you cannot add Web Reference directly. Here is how you need to do it.
From Project -> Add Service Reference ..., (From Solution Explorer, Right Click on Project, From the drop down Menu, Select Add Service Reference)
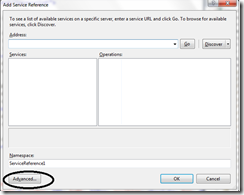
This window will appear, Click advanced,
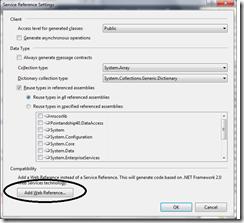
On Add Service Settings window, Now click on Add Web Reference
This will open add Web reference window from where we can add web service. Hope this helps. Good luck.